Part 1: Trauma and the Soul: Understanding Its Impact on Thoughts, Emotions, and Behaviours
By Susan Adeyemi, Counsellor, & Author

- What is Trauma?
- Statistics in the UK
- Detailed Causes of Trauma
- Practical Indicators of Unresolved Trauma:
- Ways to Overcome
- Reflection Questions
- GET YOUR GUIDE ON MANAGING NEGATIVE EMOTIONS
- Related Articles
What is Trauma?
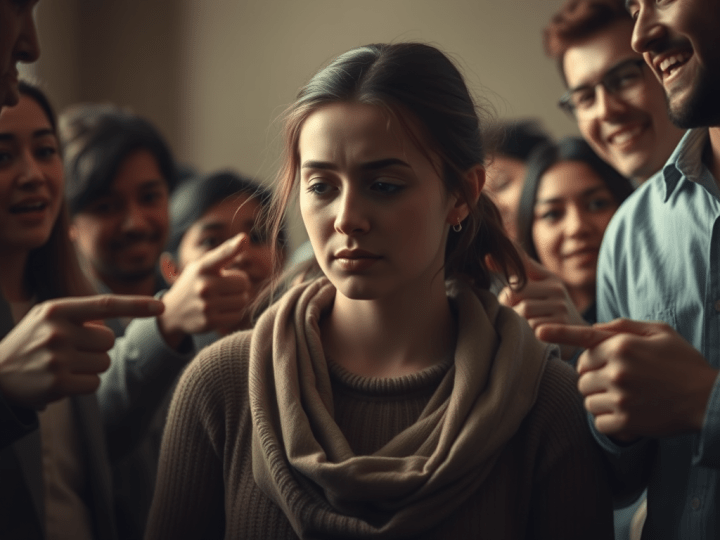
Trauma is an emotional response to deeply distressing or disturbing events that overwhelm an individual’s ability to cope, causing feelings of helplessness, diminishing their sense of self, and affecting their ability to feel a full range of emotions and experiences.
According to the NHS, trauma can occur from one-off events like accidents or assaults or ongoing stress such as abuse or neglect. Medical research by Bessel van der Kolk in “The Body Keeps the Score” highlights that trauma is not just what happens to us but how it is stored in the body and impacts our nervous system.
Scriptural Lens: The Bible acknowledges the reality of human suffering and its impact on the soul:
“The spirit of a man will sustain him in sickness, but who can bear a broken spirit?” (Proverbs 18:14, NKJV)
Statistics in the UK
Approximately 1 in 3 adults in the UK have experienced trauma during childhood (NHS Digital, Mental Health of Children and Young People in England, 2023).
A 2022 UK Trauma Council report highlighted that over 40% of adults report adverse childhood experiences, with many carrying these wounds into adulthood, affecting mental health and relationships.
Detailed Causes of Trauma
PTSD can be triggered by a variety of different events but these will always be serious. For example, events such as failing an exam, getting divorced or losing a job are not normally serious enough to trigger PTSD.
Serious events that may trigger PTSD-
◦Being a victim of personal or sexual assault
◦Being a victim of long-term sexual abuse, violence or severe neglect
◦Being involved in a bad road accident
◦Witnessing violent deaths of others such as a particularly bad accident or a suicide
◦Being involved in violent military action
◦Being held hostage
◦Witnessing or being injured in a terrorist attack
◦Being involved in a natural disaster, such as a volcanic eruption, severe flood or earthquake.
It is not clear why some people develop PTSD and others don’t but there appears to be a genetic link to the condition and those who have had anxiety or depression in the past also appear to be more at risk.
Practical Indicators of Unresolved Trauma:
- Flashbacks of past events triggered by similar sounds, smells, or environments.
- Intrusive thoughts and memories (linked to OCD)
- Emotional numbness, feeling disconnected from daily activities.
- Avoidance behaviours, such as avoiding people or situations that remind you of the trauma.
- Physical symptoms (e.g., headaches, stomach issues, sleep disturbances) without a clear medical cause.
Indicator of Unresolved Trauma – Intrusive thoughts and memories:
Intrusive symptoms are generally centred around thoughts and memories of the traumatic event and the physical symptoms associated with these thoughts and memories.
They include:
•Bad memories or recurring images of the event.
•Nightmares about the event itself or other frightening topics.
•Flashbacks which involve the individual feeling as if they are back at the time of the event and reliving it.
•Distress that occurs when something reminds the individual of the incident.
•Physical symptoms that the individual experiences when they have thoughts and flashbacks about the event. These are generally anxiety symptoms such as sweating, shaking, headaches, an increased or irregular pulse rate and breathing, and tension in the muscles.
Indicator of Unresolved Trauma – Avoidance and numbing:
Avoidance and numbing symptoms are things the individual uses to try and deal with the memories and flashbacks of the traumatic event. Individuals will try to distance themselves from the event and find ways to avoid being reminded of it.
These include:
•Avoiding any people, situations, activities, thoughts and feelings that might trigger a memory of the event. These need not be directly related to the event. For example, if it was a bright sunny day when the event occurred, any bright sunny day may trigger memories.
•Forgetting about all or part of the traumatic event and being unable to recall details of what happened and when it happened.
•Losing interest in normal activities.
•Feeling isolated and cutting themselves off from friends and family.
•Feeling numb.
•Not being able to imagine having any future.
Indicator of Unresolved Trauma – Being constantly on guard:
This is known as hypervigilance and can be stressful and exhausting for the individual. It includes:
•Constantly scanning the surroundings for potential threats.
•Overreacting to loud noises or smells connected with the traumatic incident.
•Becoming irritated and agitated in crowds or other situations where they feel there is too much to analyse.
•Being angry and irritable.
•Reading too much into situations and over-scrutinising things.
•Being constantly concerned about others.
•Being distracted and unable to focus.
Example Scenario:
Sarah, a 35-year-old mother, notices she feels panicked whenever her husband raises his voice, even if he is not angry with her. She feels her heart racing, her mind goes blank, and she feels like a “small child again.” She avoids conversations when conflict arises, fearing abandonment.
Ways to Overcome
Awareness: Acknowledge that these reactions are linked to past trauma, not just the current situation.
– Grounding exercises: Breathing deeply while saying, “I am safe now, this is not then.”
– Scripture Meditation: Reflect on Psalm 34:18: “The Lord is close to the brokenhearted and saves those who are crushed in spirit.”
– Seek Support: Speaking with a Christian counsellor can help process fear safely.
Reflection Questions
- Have you considered how past events may still influence your thoughts and reactions today?
- What areas of your life feel heavy or “stuck,” indicating unprocessed pain?
Use the GUIDE BELOW to evaluate your emotions. It also offers practical and biblical methods to manage negative emotions.
GET YOUR GUIDE ON MANAGING NEGATIVE EMOTIONS
Share your story in the comments and with others.
Your experience can bring light and encouragement to someone else navigating the same struggle. If this post helped you, share it with a friend who may be silently battling fear